Cybersecurity is a good career option for people that want to make money, don’t need a lot of socialization on the job and enjoy solving logic based problems. It has a high salary, low unemployment rate and plenty of opportunities to grow and learn new things.
Cybersecurity is the protection of computer systems and networks from attacks that could result in unauthorized access to data. Attacks can cause damage to business operations, disrupting service delivery and impacting the economy.
Why Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the application of technology, processes, and controls to protect systems, networks, programs, devices, and data from unauthorized digital access or attack. Attacks can have devastating impacts on businesses and individuals, resulting in lost revenue, stolen intellectual property, compromised personal data, and damaged reputations. Cyberattacks are more frequent and more sophisticated, with attackers using an ever-expanding list of tactics.
A career in cybersecurity requires a broad skill set to be successful, including knowledge of networking, software, hardware, and databases. In addition, cybersecurity professionals should have good critical thinking skills and be able to remain calm under pressure. They must also be willing to learn and adapt as the threat landscape continues to change.
As a Cybersecurity professional, you’ll be responsible for protecting three main entities: endpoints such as computers and Internet of Things (IoT) devices; networks; and the cloud. You’ll need to understand how each of these functions and the tools needed to protect them, including encryption, access management, network and transmission control protocols, and security information event management (SIEM) tools.
You’ll also be required to have a strong understanding of data protection and privacy laws. Finally, a career in cybersecurity requires the ability to communicate with others both written and verbally. This is because you’ll be part of a team that needs to work together to identify and mitigate threats.
It pays well
Cybersecurity is a fast-growing field that offers lucrative compensation. The top-paying jobs typically pay over $100,000, and some senior positions can earn up to $400,000 or more. However, salary levels vary by location and job responsibilities. It’s important to consider these factors when deciding whether cybersecurity is a good career choice for you.
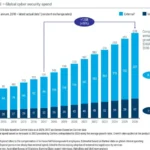
As hackers continue to evolve and find new ways to breach cyberinfrastructure, the demand for cybersecurity professionals is growing. Many states have a high concentration of cyber security jobs, and salaries are significantly higher in cities where there are more tech companies and other industries that require data protection.
The best way to start a career in cyber security is to obtain a bachelor’s degree in computer science or information technology. This can help you build a solid foundation of knowledge and prepare for more advanced training or professional certifications. However, if you want to get into the field quickly, an associate degree might be enough for you.
Another option is to attend a cybersecurity boot camp, which is a shorter program that can give you the skills you need to succeed in the field. These programs also provide you with practical learning and real-world experience. In addition, some of these boot camps have a partnership with leading IT organizations and can help you find a job once you graduate.
It’s a technology based field
Cyber security is a field that requires a lot of technical skills. This includes a strong understanding of the CIA Triad (confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility). It also requires a knowledge of network architecture, Linux systems, and threat detection tools. In addition, cybersecurity professionals need to know how to protect endpoint devices like computers and smart devices. This may include firewalls, antivirus software, and VPNs.
Cybercriminals are constantly developing new techniques to access and damage information systems and data networks. These attacks can be devastating for companies and their customers. They can also compromise critical infrastructure like power plants and hospitals. They can also impact your personal life by stealing your personal data or compromising your financial security.
The good news is that cybersecurity has a lot of career paths available to tech-savvy people. You can choose to specialise in the areas that interest you the most. Depending on your background, you can move towards security engineering and architecture, or become an ethical hacker or digital forensic investigator.
You can also pursue a leadership role by becoming a security manager or cybersecurity chief. However, the most popular careers in cybersecurity are in risk management and incident response. Licensure and certification are also available to help you progress in your chosen path. You can obtain these credentials through professional organizations and governmental bodies.
It’s not a social career
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting internet-connected systems, software, and data from cyber attacks. It’s becoming increasingly important as our world becomes more reliant on technology, and hackers find new ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Advanced cybersecurity measures can help prevent these attacks, minimizing the risk of data breaches and other financial losses. They can also protect critical infrastructure systems such as power grids and transportation networks from disruptions that could affect public safety or national security.
Many companies are putting more resources into cybersecurity due to the increased awareness of how serious a problem it can be. However, it’s not an easy job. It’s often stressful because it requires a lot of attention and effort to keep up with the constant threat landscape. It’s also not a profit center for most businesses so they may feel reluctant to spend money on it.
Another reason why cybersecurity might not be for everyone is that it’s a very technical career. But it is worth mentioning that there are jobs in cybersecurity that don’t require much, if any, technical knowledge. These include positions such as product managers, user interface designers, and analysts who perform a lot of research and data science work. There are also non-technical roles that are growing in demand, such as legal professionals who focus on privacy and security concerns, and consultants who advise companies regarding their security posture.